Overview of Hazardous Areas

What is a Hazardous Area?
Hazardous Area Classification
Hazardous areas are defined as:
• “Divisions” under North American NEC standards.
- Under the “Zone” system, hazards are defined for gas as Zone 0, 1 or 2, with 0 as the highest hazard, and for dust as Zone 20, 21 or 22, with 20 as the highest hazard.
- Under the “Division” system, hazards are defined for gas as Class I Division 1 or 2, with 1 as the highest hazard, and for dust as Class II Division 1 or 2, with 1 as the highest hazard.

- Zone 0/20: > 1000 hours /year
- Zone 1/21: 10 to 1000 hours/year
- Zone 2/22: < 10 hours/year
- Class I & II Div 1: > 10 hours /year
- Class I & II Div 2: < 10 hours/year
Codes and Standards
- Worldwide: IEC defines the most-widely adopted hazardous area standards.
- In Europe, the ATEX scheme closely follows IEC standards
- In North America: the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) is the primary agency for the protection of installations from fire and explosion.
For full hazardous area information, download our Hazardous Location Chart from the Resources section
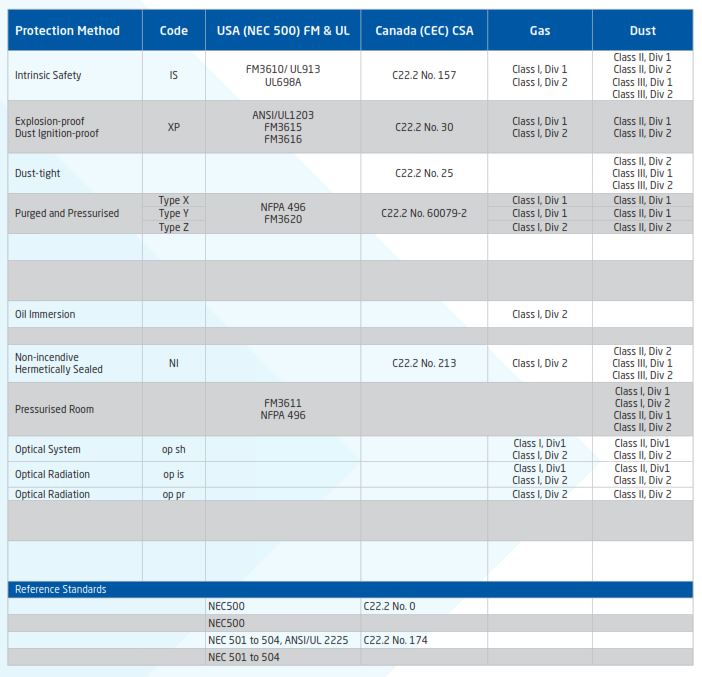
Recognised Methods for Explosion Protection
- Explosive material is present in a suitable concentration
- The presence of air or oxygen
- A source of ignition

Under the various codes and standards, there are a number of recognised methods for explosion protection.

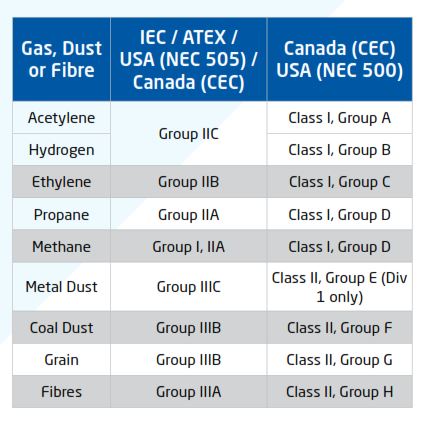
Classification of flammable materials
Group definitions may vary between certification schemes.
For full hazardous area information, download our Hazardous Location Chart from the Resources section
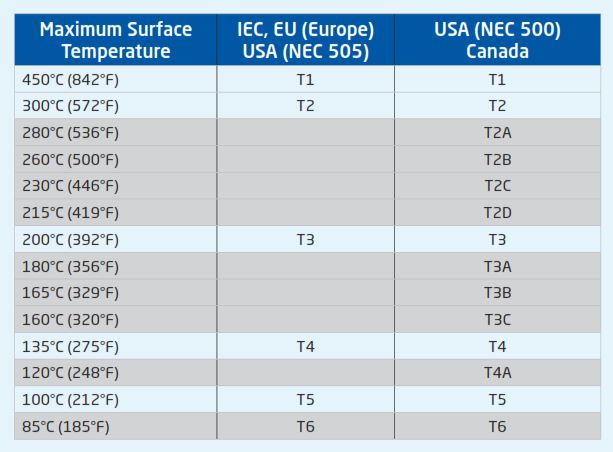
Temperature Classification
Temperature classification (also known as temperature class, or T class) defines the maximum surface temperature that a product destined for use in a potentially hazardous atmosphere is allowed to operate at, relative to an ambient temperature of -20°C to +40°C.
All flammable gases have an auto-ignition temperature. If a flammable mixture of the gas is exposed to a component above the auto-ignition temperature, then the mixture will ignite. Therefore, when selecting equipment, the Temperature class must be below the auto-ignition temperature of the potentially explosive atmosphere where it will be installed.
For full hazardous area information, download our Hazardous Location Chart from the Resources section



